Most organizations go through an organizational redesign to:
- Better align to the strategic objectives of the organization.
- Increase the effectiveness of IT as a function.
- Provide employees with clarity in their roles and responsibilities.
- Support new capabilities.
- Better align IT capabilities to suit the vision.
- Ensure the IT organization can support transformation initiatives.
Our Advice
Critical Insight
- Organizational redesign is only as successful as the process leaders engage in. It shapes a story framed in a strong foundation of need and a method to successfully implement and adopt the new structure.
- Benchmarking your organizational redesign to other organizations will not work. Other organizations have different strategies, drivers, and context. It’s important to focus on your organization, not someone else's.
- You could have the best IT employees in the world, but if they aren’t structured well your organization will still fail in reaching its vision.
Impact and Result
- We are often unsuccessful in organizational redesign because we lack an understanding of why this initiative is required or fail to recognize that it is a change initiative.
- Successful organizational design requires a clear understanding of why it is needed and what will be achieved by operating in a new structure.
- Additionally, understanding the impact of the change initiative can lead to greater adoption by core stakeholders.
Member Testimonials
After each Info-Tech experience, we ask our members to quantify the real-time savings, monetary impact, and project improvements our research helped them achieve. See our top member experiences for this blueprint and what our clients have to say.
9.2/10
Overall Impact
$67,383
Average $ Saved
24
Average Days Saved
Client
Experience
Impact
$ Saved
Days Saved
Mencap
Guided Implementation
9/10
$9,000
5
Hume City Council
Guided Implementation
10/10
$23,649
12
Duquesne University
Workshop
10/10
$6,499
32
Alabama Department of Environmental Management
Workshop
10/10
N/A
10
Hume City Council
Guided Implementation
10/10
$18,849
5
Feld Entertainment, Inc.
Guided Implementation
10/10
N/A
N/A
Arizona Department of Environmental Quality
Guided Implementation
10/10
$129K
50
Kitsap Credit Union
Workshop
10/10
$11,699
20
District Municipality Of Muskoka
Workshop
10/10
$8,000
14
Municipality of Chatham-Kent
Guided Implementation
8/10
N/A
N/A
Community Health Choice, Inc.
Workshop
10/10
N/A
N/A
Institute of Public Accountants
Guided Implementation
9/10
N/A
N/A
The Corporation of the City of Kingston
Workshop
8/10
$50,000
35
Alabama Department of Labor (ADOL)
Workshop
10/10
$129K
20
SUNS LEGACY PARTNERS, LLC
Guided Implementation
10/10
$12,999
23
Earlham College
Guided Implementation
8/10
$12,999
1
Transport Canada
Workshop
8/10
$10,000
5
Al-Amthal Financing Company
Guided Implementation
8/10
$14,500
10
Correctional Service of Canada
Workshop
8/10
$70,000
10
Office of the Superintendent of Financial Institutions Canada
Workshop
9/10
$500K
100
Darling Ingredients
Workshop
9/10
$32,499
10
Seattle Housing Authority
Workshop
8/10
N/A
N/A
University Of North Dakota
Workshop
9/10
$32,499
20
Milwaukee County Department of Administrative Services – Information Management Division (DAS-IMSD)
Workshop
10/10
N/A
N/A
Reserve Bank of Australia
Workshop
10/10
$171K
110
SA Power Networks
Guided Implementation
9/10
$12,313
5
Rosemont Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Guided Implementation
10/10
$3,116
5
City of Bloomington, IL
Guided Implementation
10/10
$32,499
10
ReSource Pro
Guided Implementation
10/10
$64,999
4
Apotex
Workshop
8/10
$100K
10

IT Organizational Design
Note: This course will be updated in July 2023.
Improve performance through a fit-for-purpose organizational design.
This course makes up part of the People & Resources Certificate.
- Course Modules: 5
- Estimated Completion Time: 2-2.5 hours
- Featured Analysts:
- Carlene McCubbin, Sr. Research Manager, CIO Practice
- James Alexander, SVP of Research and Advisory, CIO Practice
Workshop: Redesign Your IT Organizational Structure
Workshops offer an easy way to accelerate your project. If you are unable to do the project yourself, and a Guided Implementation isn't enough, we offer low-cost delivery of our project workshops. We take you through every phase of your project and ensure that you have a roadmap in place to complete your project successfully.
Module 1: Establish the Organizational Design Foundation
The Purpose
- Lay the foundation for your organizational redesign by establishing a set of organizational design principles that will guide the redesign process.
Key Benefits Achieved
- Clearly articulate why this organizational redesign is needed and the implications the strategies and context will have on your structure.
Activities
Outputs
Define the org design drivers.
- Clear definition of the need to redesign the organizational structure
Document and define the implications of the business context.
- Understanding of the business context implications on the organizational structure creation.
Align the structure to support the strategy.
- Strategic impact of strategies on organizational design.
Establish guidelines to direct the organizational design process.
- Customized Design Principles to rationalize and guide the organizational design process.
Module 2: Create the Operating Model Sketch
The Purpose
Select and customize an operating model sketch that will accurately reflect the future state your organization is striving towards. Consider how capabilities will be sourced, gaps in delivery, and alignment.
Key Benefits Achieved
- A customized operating model sketch that informs what capabilities will make up your IT organization and how those capabilities will align to deliver value to your organization.
Activities
Outputs
Augmented list of IT capabilities.
- Customized list of IT processes that make up your organization.
Capability gap analysis
- Analysis of which capabilities require dedicated focus in order to meet goals.
Identified capabilities for outsourcing.
- Definition of why capabilities will be outsourced and the method of outsourcing used to deliver the most value.
Select a base operating model sketch.
- Customized IT operating model reflecting sourcing, centralization, and intended delivery of value.
Customize the IT operating model sketch.
Module 3: Formalize the Organizational Structure
The Purpose
Translate the operating model sketch into a formal structure with defined functional teams, roles, reporting structure, and responsibilities.
Key Benefits Achieved
- A detailed organizational chart reflecting team structures, reporting structures, and role responsibilities.
Activities
Outputs
Categorize your IT capabilities within your defined functional work units.
- Capabilities Organized Into Functional Groups
Create a mandate statement for each work unit.
- Functional Work Unit Mandates
Define roles inside the work units and assign accountability and responsibility.
Finalize your organizational structure.
- Organizational Chart
Module 4: Plan for the Implementation & Change
The Purpose
Ensure the successful implementation of the new organizational structure by strategically communicating and involving stakeholders.
Key Benefits Achieved
- A clear plan of action on how to transition to the new structure, communicate the new organizational structure, and measure the effectiveness of the new structure.
Activities
Outputs
Identify and mitigate key org design risks.
- Risk Mitigation Plan
Define the transition plan.
Create the change communication message.
- Change Communication Message
Create a standard set of FAQs.
- Standard FAQs
Align sustainment metrics back to core drivers.
- Implementation and sustainment metrics.
Redesign Your IT Organizational Structure
Designing an IT structure that will enable your strategic vision is not about an org chart – it’s about how you work.
EXECUTIVE BRIEF
Analyst Perspective
Structure enables strategy.

Allison Straker
Research Director,
Organizational Transformation

Brittany Lutes
Senior Research Analyst,
Organizational Transformation
An organizational structure is much more than a chart with titles and names. It defines the way that the organization operates on a day-to-day basis to enable the successful delivery of the organization’s information and technology objectives. Moreover, organizational design sees beyond the people that might be performing a specific role. People and role titles will and often do change frequently. Those are the dynamic elements of organizational design that allow your organization to scale and meet specific objectives at defined points of time. Capabilities, on the other hand, are focused and related to specific IT processes.
Redesigning an IT organizational structure can be a small or large change transformation for your organization. Create a structure that is equally mindful of the opportunities and the constraints that might exist and ensure it will drive the organization towards its vision with a successful implementation. If everyone understands why the IT organization needs to be structured that way, they are more likely to support and adopt the behaviors required to operate in the new structure.
Executive Summary
Your Challenge
Your organization needs to reorganize itself because:
- The current IT structure does not align to the strategic objectives of the organization.
- There are inefficiencies in how the IT function is currently operating.
- IT employees are unclear about their role and responsibilities, leading to inconsistencies.
- New capabilities or a change in how the capabilities are organized is required to support the transformation.
Common Obstacles
Many organizations struggle when it comes redesigning their IT organizational structure because they:
- Jump right into creating the new organizational chart.
- Do not include the members of the IT leadership team in the changes.
- Do not include the business in the changes.
- Consider the context in which the change will take place and how to enable successful adoption.
Info-Tech’s Approach
Successful IT organization redesign includes:
- Understanding the drivers, context, and strategies that will inform the structure.
- Remaining objective by focusing on capabilities over people or roles.
- Identifying gaps in delivery, sourcing strategies, customers, and degrees of centralization.
- Remembering that organizational design is a change initiative and will require buy-in.
Info-Tech Insight
A successful redesign requires a strong foundation and a plan to ensure successful adoption. Without these, the organizational chart has little meaning or value.
Your challenge
This research is designed to help organizations who are looking to:
- Redesign the IT structure to align to the strategic objectives of the enterprise.
- Increase the effectiveness in how the IT function is operating in the organization.
- Provide clarity to employees around their roles and responsibilities.
- Ensure there is an ability to support new IT capabilities and/or align capabilities to better support the direction of the organization.
- Align the IT organization to support a business transformation such as becoming digitally enabled or engaging in M&A activities.
Organizational design is a challenge for many IT and digital executives
69% of digital executives surveyed indicated challenges related to structure, team silos, business-IT alignment, and required roles when executing on a digital strategy.
Source: MIT Sloan, 2020
Common obstacles
These barriers make IT organizational redesign difficult to address for many organizations:
- Confuse organizational design and organizational charts as the same thing.
- Start with the organizational chart, not taking into consideration the foundational elements that will make that chart successful.
- Fail to treat organizational redesign as a change management initiative and follow through with the change.
- Exclude impacted or influential IT leaders and/or business stakeholders from the redesign process.
- Leverage an operating model because it is trending.
To overcome these barriers:
- Understand the context in which the changes will take place.
- Communicate the changes to those impacted to enable successful adoption and implementation of a new organizational structure.
- Understand that organizational design is for more than just HR leaders now; IT executives should be driving this change.
Succeed in Organizational Redesign
75% The percentage of change efforts that fail.
Source: TLNT, 2019
55% The percentage of practitioners who identify how information flows between work units as a challenge for their organization.
Source: Journal of Organizational Design, 2019
Organizational design defined
If your IT strategy is your map, your IT organizational design represents the optimal path to get there.
IT organizational design refers to the process of aligning the organization’s structure, processes, metrics, and talent to the organization’s strategic plan to drive efficiency and effectiveness.
Why is the right IT organizational design so critical to success? |
||
Adaptability is at the core of staying competitive today |
Structure is not just an organizational chart |
Organizational design is a never-ending process |
Digital technology and information transparency are driving organizations to reorganize around customer responsiveness. To remain relevant and competitive, your organizational design must be forward looking and ready to adapt to rapid pivots in technology or customer demand. |
The design of your organization dictates how roles function. If not aligned to the strategic direction, the structure will act as a bungee cord and pull the organization back toward its old strategic direction (ResearchGate.net, 2014). Structure supports strategy, but strategy also follows structure. |
Organization design is not a one-time project but a continuous, dynamic process of organizational self-learning and continuous improvement. Landing on the right operating model will provide a solid foundation to build upon as the organization adapts to new challenges and opportunities. |
Understand the organizational differences
Organizational Design
Organizational design the process in which you intentionally align the organizational structure to the strategy. It considers the way in which the organization should operate and purposely aligns to the enterprise vision. This process often considers centralization, sourcing, span of control, specialization, authority, and how those all impact or are impacted by the strategic goals.
Operating Model
Operating models provide an architectural blueprint of how IT capabilities are organized to deliver value. The placement of the capabilities can alter the culture, delivery of the strategic vision, governance model, team focus, role responsibility, and more. Operating model sketches should be foundational to the organizational design process, providing consistency through org chart changes.
Organizational Structure
The organizational structure is the chosen way of aligning the core processes to deliver. This can be strategic, or it can be ad hoc. We recommend you take a strategic approach unless ad hoc aligns to your culture and delivery method. A good organizational structure will include: “someone with authority to make the decisions, a division of labor and a set of rules by which the organization operates” (Bizfluent, 2019).
Organizational Chart
The capstone of this change initiative is an easy-to-read chart that visualizes the roles and reporting structure. Most organizations use this to depict where individuals fit into the organization and if there are vacancies. While this should be informed by the structure it does not necessarily depict workflows that will take place. Moreover, this is the output of the organizational design process.
Sources: Bizfluent, 2019; Strategy & Business, 2015; SHRM, 2021
The Technology Value Trinity
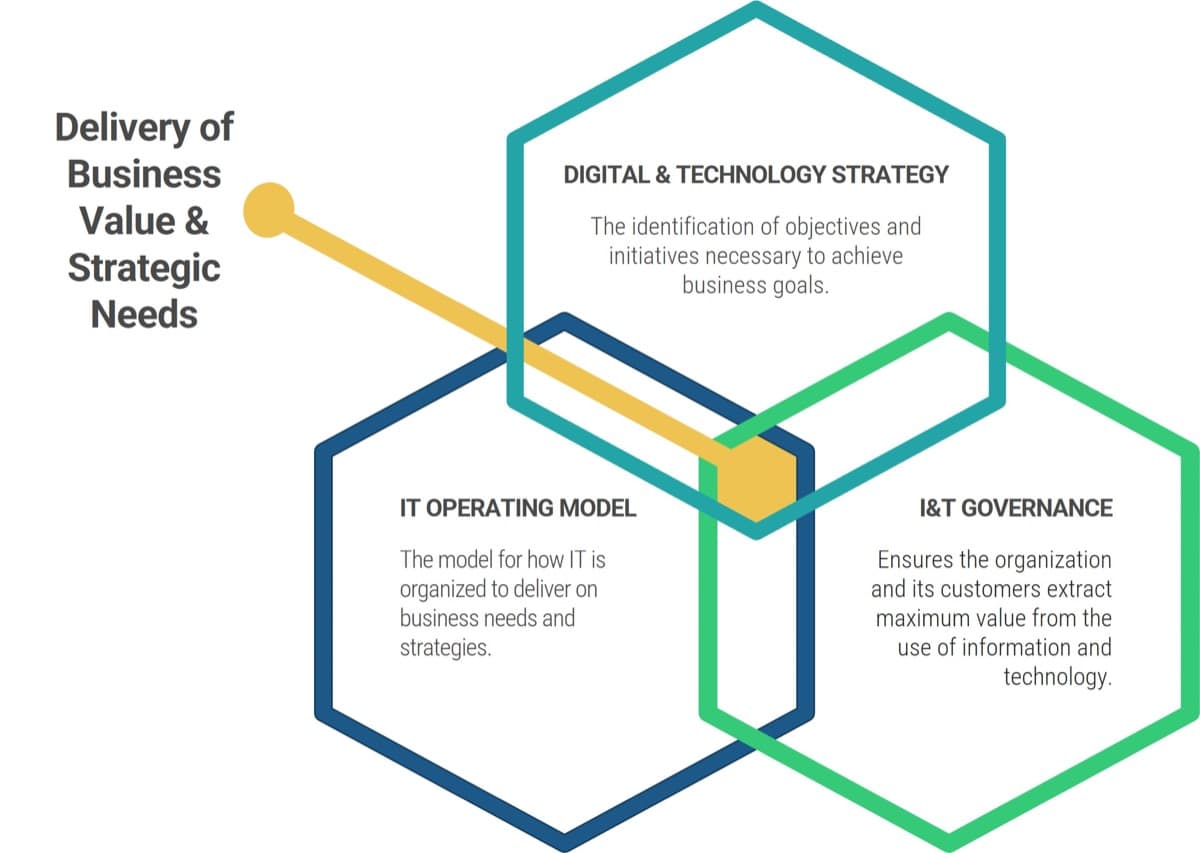
All three elements of the Technology Value Trinity work in harmony to delivery business value and achieve strategic needs. As one changes, the others need to change as well.
How do these three elements relate?
- Digital and IT strategy tells you what you need to achieve to be successful.
- Operating model and organizational design align resources to deliver on your strategy and priorities. This is done by strategically structuring IT capabilities in a way that enables the organizations vision and considers the context in which the structure will operate.
- I&T governance is the confirmation of IT’s goals and strategy, which ensures the alignment of IT and business strategy and is the mechanism by which you continuously prioritize work to ensure that what is delivered is in line with the strategy.
Too often strategy, organizational design, and governance are considered separate practices – strategies are defined without teams and resources to support. Structure must follow strategy.
Info-Tech’s approach to organizational design
Like a story, a strategy without a structure to deliver on it is simply words on paper.
Books begin by setting the foundation of the story.
Introduce your story by:
- Defining the need(s) that are driving this initiative forward.
- Introducing the business context in which the organizational redesign must take place.
- Outlining what’s needed in the redesign to support the organization in reaching its strategic IT goals.
The plot cannot thicken without the foundation. Your organizational structure and chart should not exist without one either.
The steps to establish your organizational chart - with functional teams, reporting structure, roles, and responsibilities defined – cannot occur without a clear definition of goals, need, and context. An organizational chart alone won’t provide the insight required to obtain buy-in or realize the necessary changes.
Conclude your story through change management and communication.
Good stories don’t end without referencing what happened before. Use the literary technique of foreshadowing – your change management must be embedded throughout the organizational redesign process. This will increase the likelihood that the organizational structure can be communicated, implemented, and reinforced by stakeholders.
Info-Tech uses a capability-based approach to help you design your organizational structure
Once your IT strategy is defined, it is critical to identify the capabilities that are required to deliver on those strategic initiatives. Each initiative will require a combination of these capabilities that are only supported through the appropriate organization of roles, skills, and team structures.
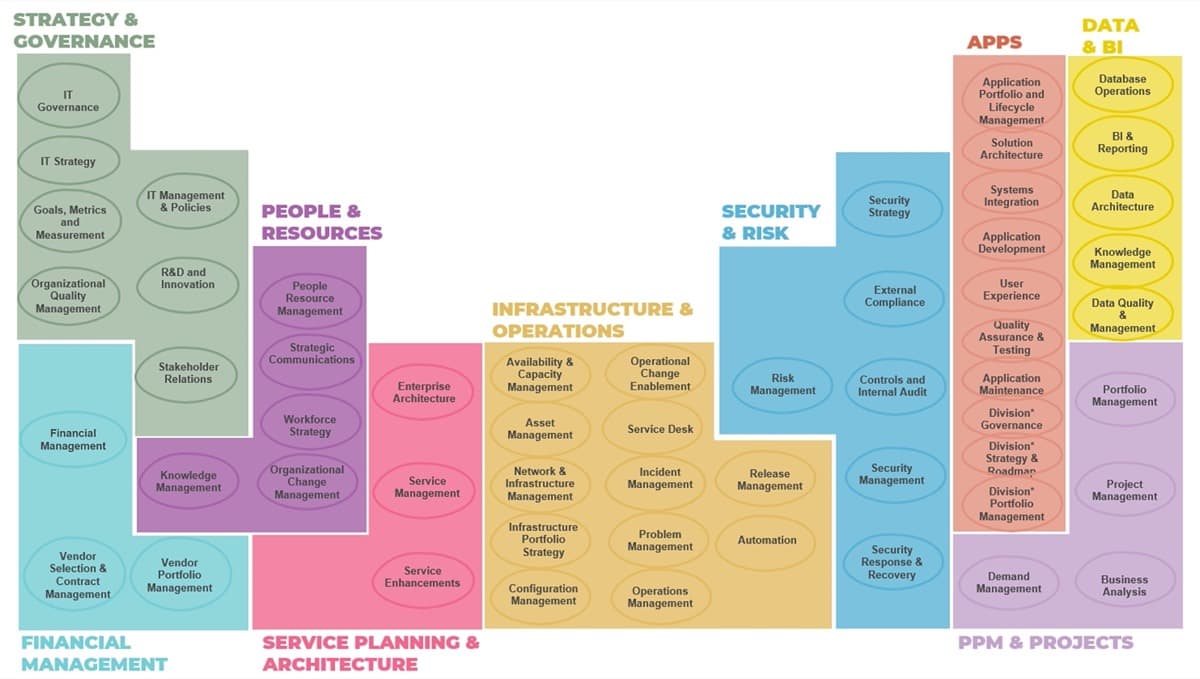
Embed change management into organizational design
Change management practices are needed from the onset to ensure the implementation of an organizational structure.
For each phase of this blueprint, its important to consider change management. These are the points when you need to communicate the structure changes:
- Phase 1: Begin to socialize the idea of new organizational structure with executive leadership and explain how it might be impactful to the context of the organization. For example, a new control, governance model, or sourcing approach could be considered.
- Phase 2: The chosen operating model will influence your relationships with the business and can create/eliminate silos. Ensure IT and business leaders have insight into these possible changes and a willingness to move forward.
- Phase 3: The new organizational structure could create or eliminate teams, reduce or increase role responsibilities, and create different reporting structures than before. It’s time to communicate these changes with those most impacted and be able to highlight the positive outcomes of the various changes.
- Phase 4: Should consider the change management practices holistically. This includes the type of change and length of time to reach the end state, communication, addressing active resistors, acquiring the right skills, and measuring the success of the new structure and its adoption.
Info-Tech Insight
Do not undertake an organizational redesign initiative if you will not engage in change management practices that are required to ensure its successful adoption.
Measure the value of the IT organizational redesign
Given that the organizational redesign is intended to align with the overall vision and objectives of the business, many of the metrics that support its success will be tied to the business. Adapt the key performance indicators (KPIs) that the business is using to track its success and demonstrate how IT can enable the business and improve its ability to reach those targets.
Strategic Resources
The percentage of resources dedicated to strategic priorities and initiatives supported by IT operating model. While operational resources are necessary, ensuring people are allocating time to strategic initiatives as well will drive the business towards its goal state. Leverage Info-Tech’s IT Staffing Assessment diagnostic to benchmark your IT resource allocation.
Business Satisfaction
Assess the improvement in business satisfaction overall with IT year over year to ensure the new structure continues to drive satisfaction across all business functions. Leverage Info-Tech’s CIO Business Vision diagnostic to see how your IT organization is perceived.
Role Clarity
The degree of clarity that IT employees have around their role and its core responsibilities can lead to employee engagement and retention. Consider measuring this core job driver by leveraging Info-Tech’s Employee Engagement Program.
Customer & User Satisfaction
Measure customer satisfaction with technology-enabled business services or products and improvements in technology-enabled client acquisition or retention processes. Assess the percentage of users satisfied with the quality of IT service delivery and leverage Info-Tech’s End-User Satisfaction Survey to determine improvements.
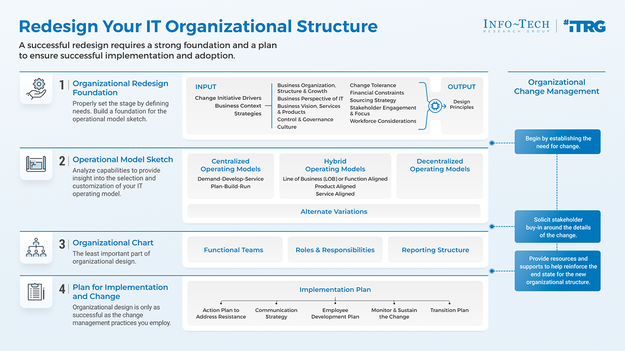
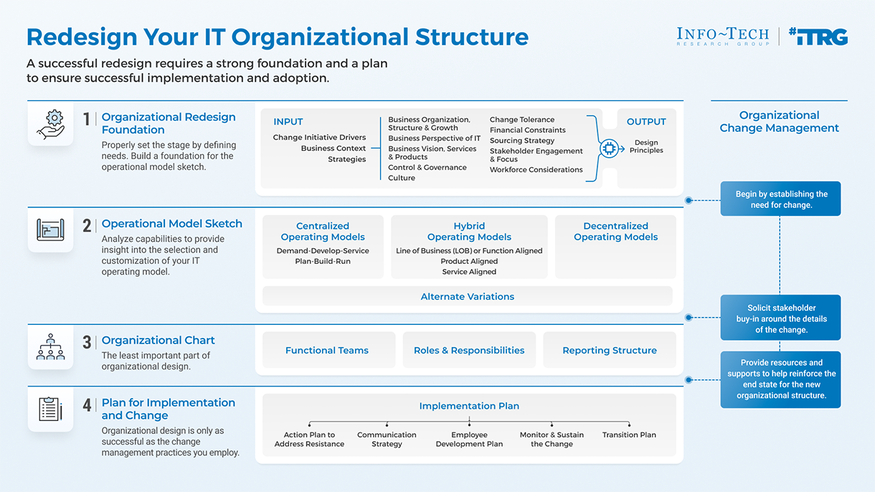
Info-Tech’s methodology for Redesigning Your IT Organization
Phase |
1. Establish the Organizational Design Foundation |
2. Create the Operating Model Sketch |
3. Formalize the Organizational Structure |
4. Plan for Implementation and Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Phase Outcomes |
Lay the foundation for your organizational redesign by establishing a set of organizational design principles that will guide the redesign process. |
Select and customize an operating model sketch that will accurately reflect the future state your organization is striving towards. Consider how capabilities will be sourced, gaps in delivery, and alignment. |
Translate the operating model sketch into a formal structure with defined functional teams, roles, reporting structure, and responsibilities. |
Ensure the successful implementation of the new organizational structure by strategically communicating and involving stakeholders. |
Insight summary
Overarching insight
Organizational redesign processes focus on defining the ways in which you want to operate and deliver on your strategy – something an organizational chart will never be able to convey.
Phase 1 insight
Focus on your organization, not someone else's’. Benchmarking your organizational redesign to other organizations will not work. Other organizations have different strategies, drivers, and context.
Phase 2 insight
An operating model sketch that is customized to your organization’s specific situation and objectives will significantly increase the chances of creating a purposeful organizational structure.
Phase 3 insight
If you follow the steps outlined in the first three phases, creating your new organizational chart should be one of the fastest activities.
Phase 4 insight
Throughout the creation of a new organizational design structure, it is critical to involve the individuals and teams that will be impacted.
Tactical insight
You could have the best IT employees in the world, but if they aren’t structured well your organization will still fail in reaching its vision.
Blueprint deliverables
Each step of this blueprint is accompanied by supporting deliverables to help you accomplish your goals:
Communication Deck
Communicate the changes to other key stakeholders such as peers, managers, and staff.
Workbook
As you work through each of the activities, use this workbook as a place to document decisions and rationale.
Reference Deck
Definitions for every capability, base operating model sketches, and sample organizational charts aligned to those operating models.
Job Descriptions
Key deliverable:
Executive Presentation
Leverage this presentation deck to gain executive buy-in for your new organizational structure.
Blueprint benefits
IT Benefits
- Create an organizational structure that aligns to the strategic goals of IT and the business.
- Provide IT employees with clarity on their roles and responsibilities to ensure the successful delivery of IT capabilities.
- Highlight and sufficiently staff IT capabilities that are critical to the organization.
- Define a sourcing strategy for IT capabilities.
- Increase employee morale and empowerment.
Business Benefits
- IT can carry out the organization’s strategic mission and vision of all technical and digital initiatives.
- Business has clarity on who and where to direct concerns or questions.
- Reduce the likelihood of turnover costs as IT employees understand their roles and its importance.
- Create a method to communicate how the organizational structure aligns with the strategic initiatives of IT.
- Increase ability to innovate the organization.
Executive Brief Case Study
IT design needs to support organizational and business objectives, not just IT needs.
INDUSTRY: Government
SOURCE: Analyst Interviews and Working Sessions
Situation
IT was tasked with providing equality to the different business functions through the delivery of shared IT services. The government created a new IT organizational structure with a focus on two areas in particular: strategic and operational support capabilities.
Challenge
When creating the new IT structure, an understanding of the complex and differing needs of the business functions was not reflected in the shared services model.
Outcome
As a result, the new organizational structure for IT did not ensure adequate meeting of business needs. Only the operational support structure was successfully adopted by the organization as it aligned to the individual business objectives. The strategic capabilities aspect was not aligned to how the various business lines viewed themselves and their objectives, causing some partners to feel neglected.
Info-Tech offers various levels of support to best suit your needs.
DIY Toolkit
"Our team has already made this critical project a priority, and we have the time and capability, but some guidance along the way would be helpful."
Guided Implementation
"Our team knows that we need to fix a process, but we need assistance to determine where to focus. Some check-ins along the way would help keep us on track."
Workshop
"We need to hit the ground running and get this project kicked off immediately. Our team has the ability to take this over once we get a framework and strategy in place."
Consulting
"Our team does not have the time or the knowledge to take this project on. We need assistance through the entirety of this project."
Diagnostics and consistent frameworks are used throughout all four options.
Guided Implementation
What does a typical GI on this topic look like?
A Guided Implementation (GI) is a series of calls with an Info-Tech analyst to help implement our best practices in your organization. A typical GI is 8 to 12 calls over the course of 4 to 6 months.
Phase 1
Call #1: Define the process, understand the need, and create a plan of action.
Phase 2
Call #2: Define org. design drivers and business context.
Call #3: Understand strategic influences and create customized design principles.
Call #4: Customize, analyze gaps, and define sourcing strategy for IT capabilities.
Call #5: Select and customize the IT operating model sketch.
Phase 3
Call #6: Establish functional work units and their mandates.
Call #7: Translate the functional organizational chart to an operational organizational chart with defined roles.
Phase 4
Call #8: Consider risks and mitigation tactics associated with the new structure and select a transition plan.
Call #9: Create your change message, FAQs, and metrics to support the implementation plan.
Workshop Overview
Contact your account representative for more information.
workshops@infotech.com 1-888-670-8889
Day 1 |
Day 2 |
Day 3 |
Day 4 |
Day 5 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Establish the Organizational Redesign Foundation |
Create the Operating Model Sketch |
Formalize the Organizational Structure |
Plan for Implementation and Change |
Next Steps and |
|
Activities |
1.1 Define the org. design drivers. 1.2 Document and define the implications of the business context. 1.3 Align the structure to support the strategy. 1.4 Establish guidelines to direct the organizational design process. |
2.1 Augment list of IT capabilities. 2.2 Analyze capability gaps. 2.3 Identify capabilities for outsourcing. 2.4 Select a base operating model sketch. 2.5 Customize the IT operating model sketch. |
3.1 Categorize your IT capabilities within your defined functional work units. 3.2 Create a mandate statement for each work unit. 3.3 Define roles inside the work units and assign accountability and responsibility. 3.4 Finalize your organizational structure. |
4.1 Identify and mitigate key org. design risks. 4.2 Define the transition plan. 4.3 Create the change communication message. 4.4 Create a standard set of FAQs. 4.5 Align sustainment metrics back to core drivers. |
5.1 Complete in-progress deliverables from previous four days. 5.2 Set up review time for workshop deliverables and to discuss next steps. |
Deliverables |
|
|
|
|
|
 Redesign Your IT Organizational Structure
Redesign Your IT Organizational Structure
 Implement a New IT Organizational Structure
Implement a New IT Organizational Structure
 Build a Strategic IT Workforce Plan
Build a Strategic IT Workforce Plan
 Optimize the IT Operating Model
Optimize the IT Operating Model
 Adopt Change Management Practices and Succeed at IT Organizational Redesign
Adopt Change Management Practices and Succeed at IT Organizational Redesign
 Fix Your IT Culture
Fix Your IT Culture
 Map Your Business Architecture to Define Your Strategy
Map Your Business Architecture to Define Your Strategy
 Implement the Next-Generation IT Operating Model
Implement the Next-Generation IT Operating Model